Consent should be given by a clear voluntary act whereby the data subject shows their agreement in a free, specific, informed and unambiguous way to the processing of their personal data.
Why is consent important?
Consent guarantees that data subjects have strong control over their data. Always associated with an obligation to inform, consent allows data subjects to understand what will be done with their data, to choose without restriction whether to accept its processing or not and to freely change their minds afterward. Consent is gathered prior to processing and can be withdrawn at any time without deteriorating the service.
Consent is one of the legal bases set out by the GDPR to authorise data processing. It is therefore one of the ways of making a processing lawful. To gather information in a valid way, four criteria must all be complied with: free, specific, informed, unambiguous. Compliance with these conditions therefore requires special attention.
Consent must be freely given
Consent must not be forced or influenced: the data subject must be offered a real choice, without suffering negative consequences in the case of refusal. The data subject must be able to refuse the processing of their data that is not necessary for the operation of the service or product they want to use, without quality of use being negatively impacted.
Example
In this example, the user has just completed a form to sign up to a service. The second stage involves the acceptance of the contract as well as use of his personal data for marketing purposes.
Focus of attention (animated example)
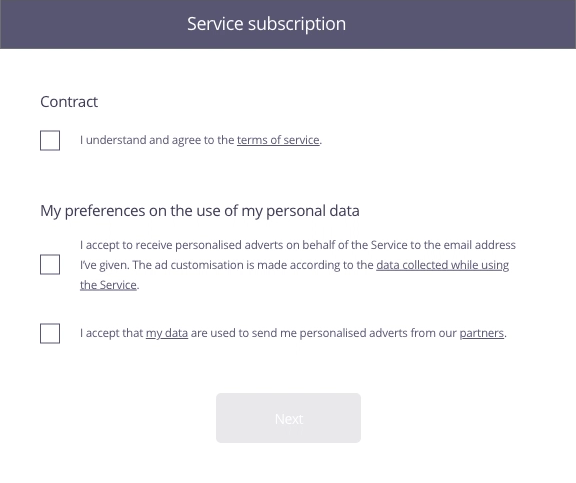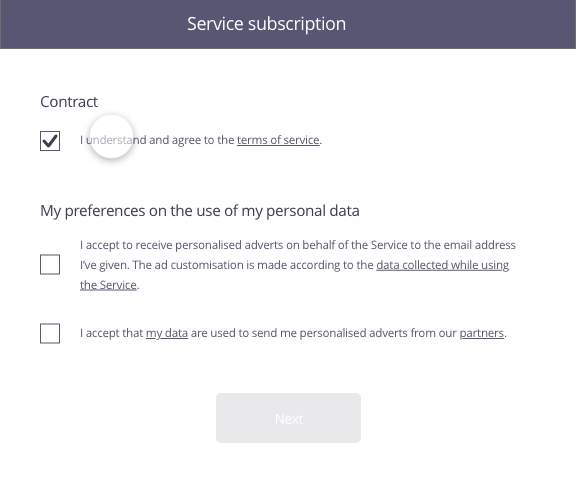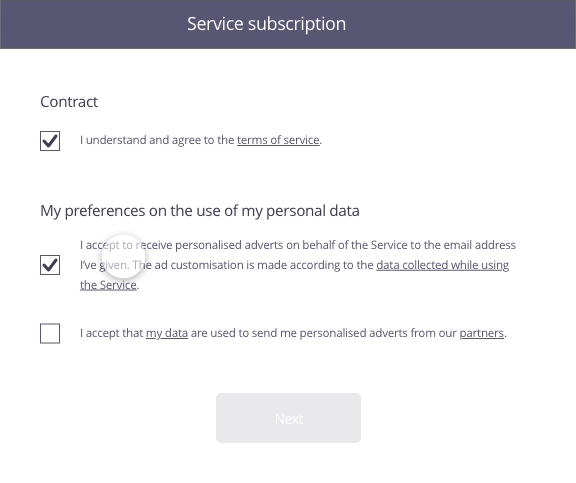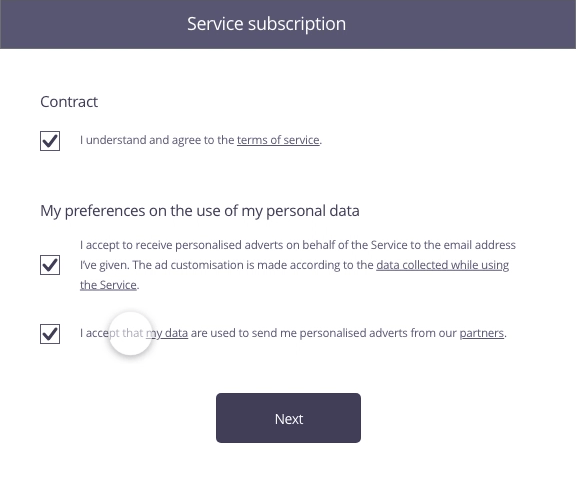
Possible approach (animated example)
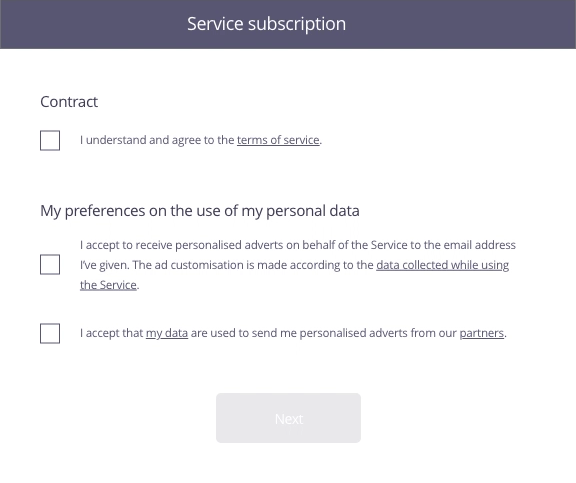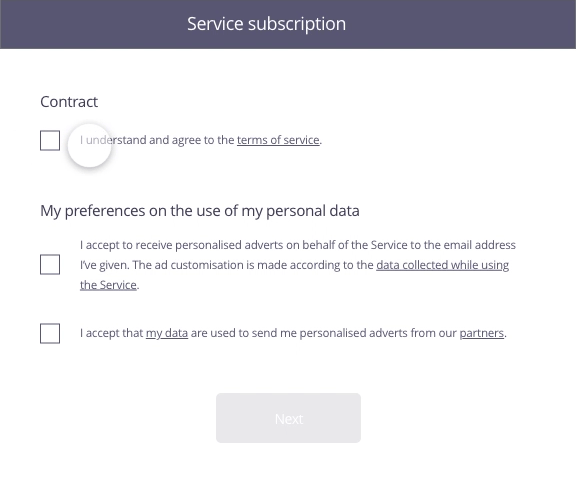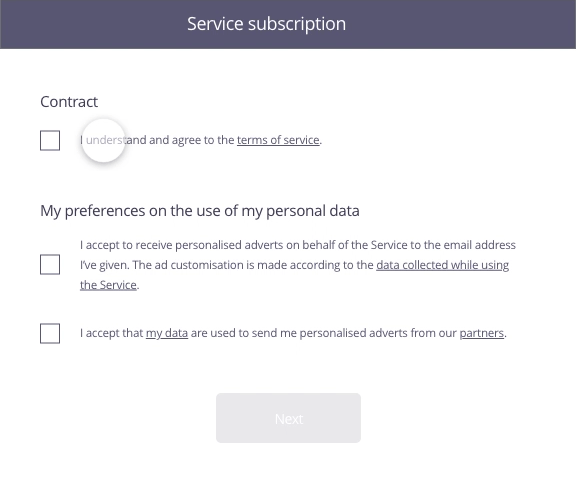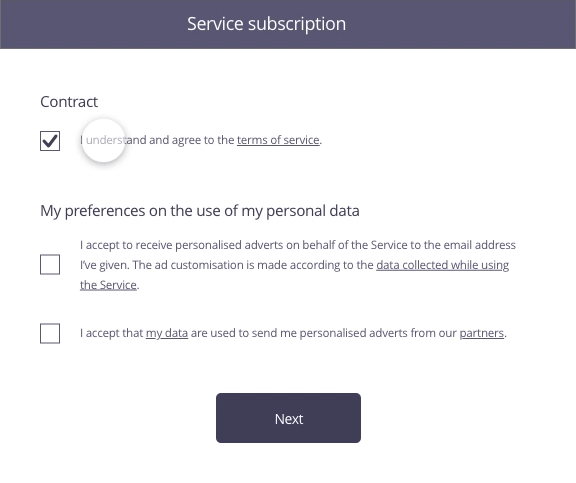
Consent must be given specifically
Consent must be given for a determined purpose. If data are used for several uses, the data subject must be able to specifically give their consent for each purpose.
Example
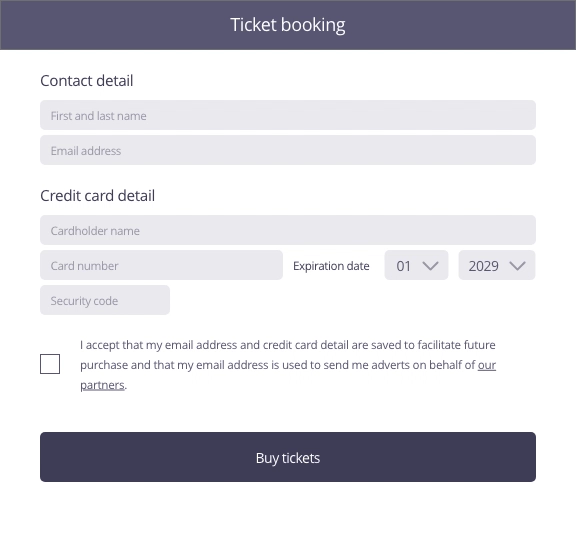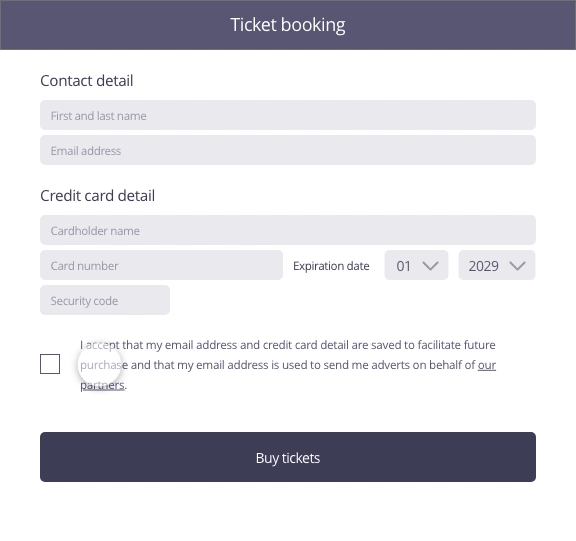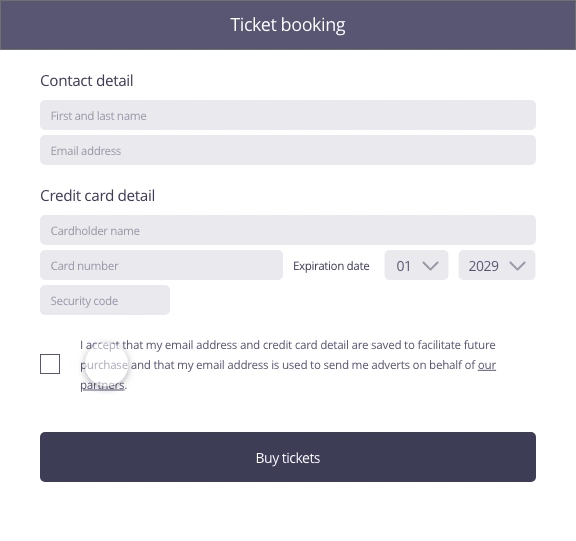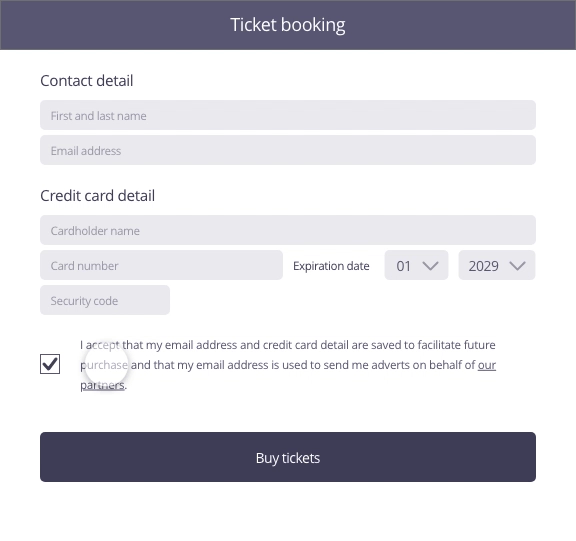
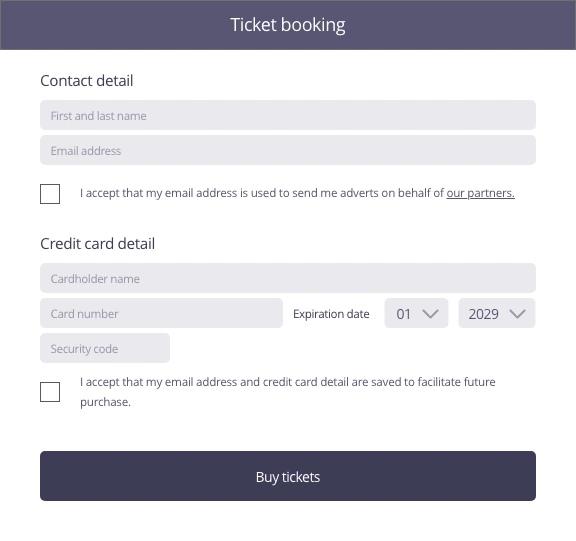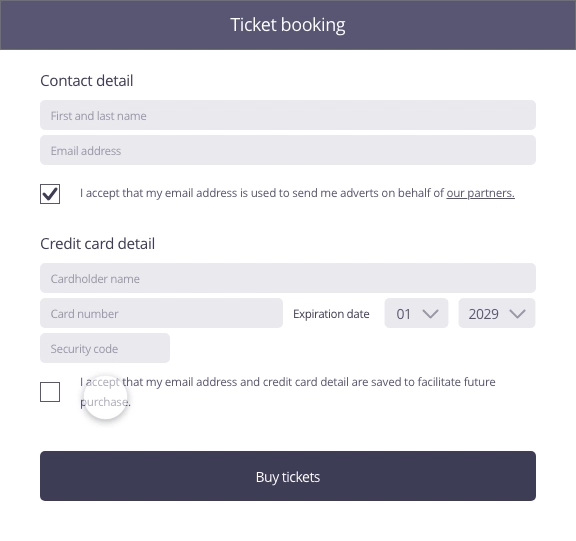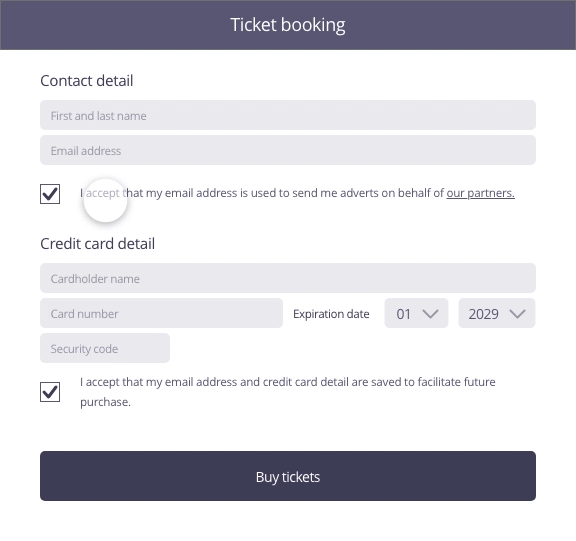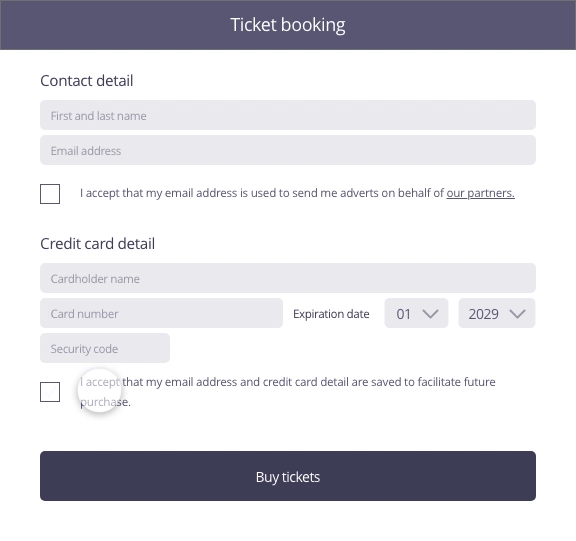
In this example, the user enters contact and payment information to buy tickets for a concert. To move to the purchasing stage by clicking on the ticket purchase button, the user is asked if he wants to save his information for easier future purchases.
Focus of attention
Possible approach (animated example)
Consent must be unambiguous
Consent requires a declaration or any other clear positive action from the data subject. She needs to take voluntary and active action to give her consent which demonstrates that she has really consented to the processing.
Consent is therefore not unambiguous in the presence of pre-ticked or pre-enabled boxes or an inaction (e.g. the absence of reply to an email requesting consent).
Example
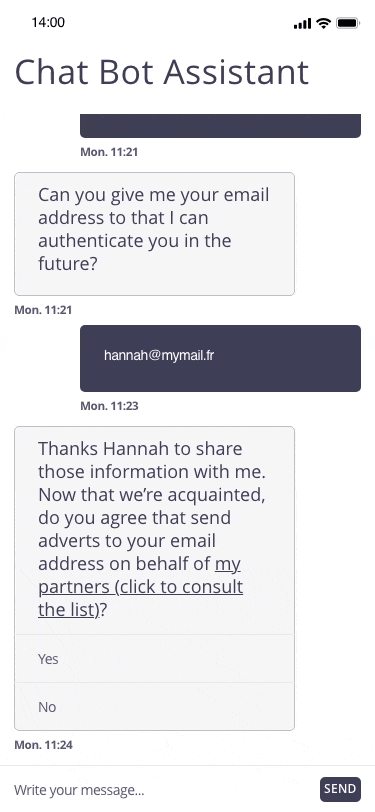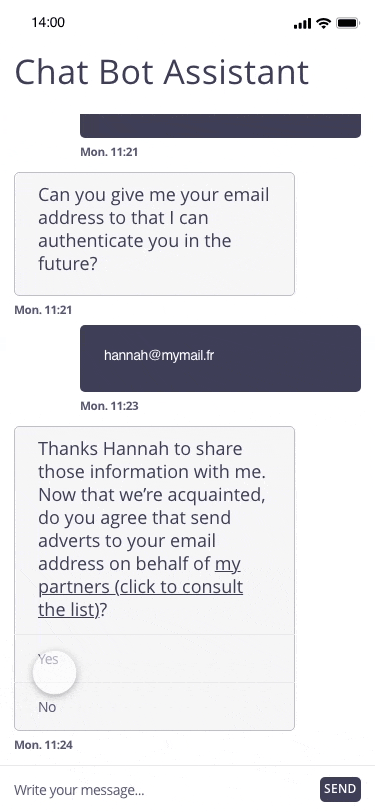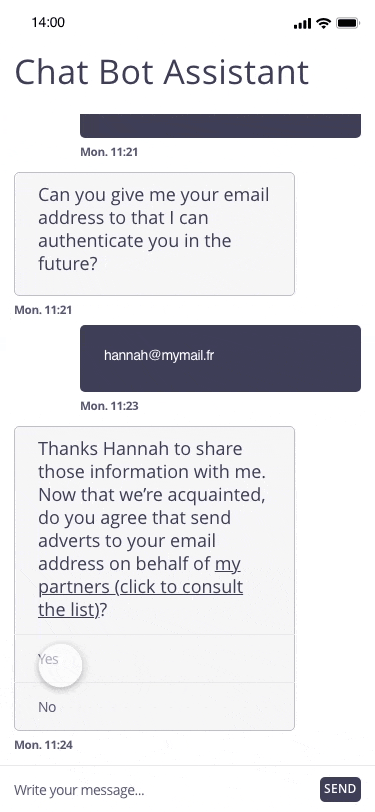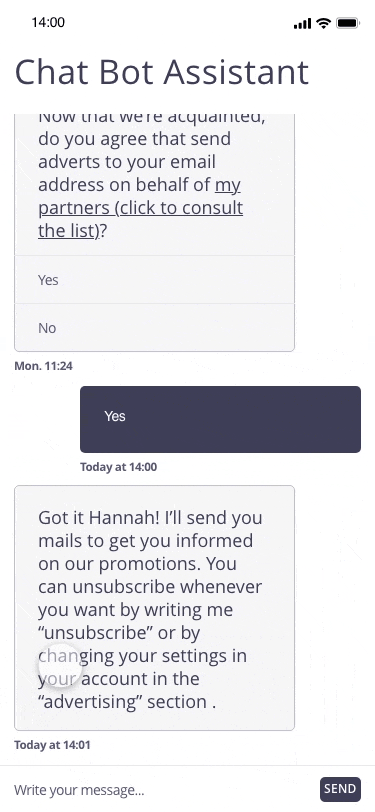
In this example, the user registers for a personal assistant service through a related chatbot. At the end of the registration, the chatbot proposes to regularly send marketing emails to the email address communicated by the user.
Focus of attention
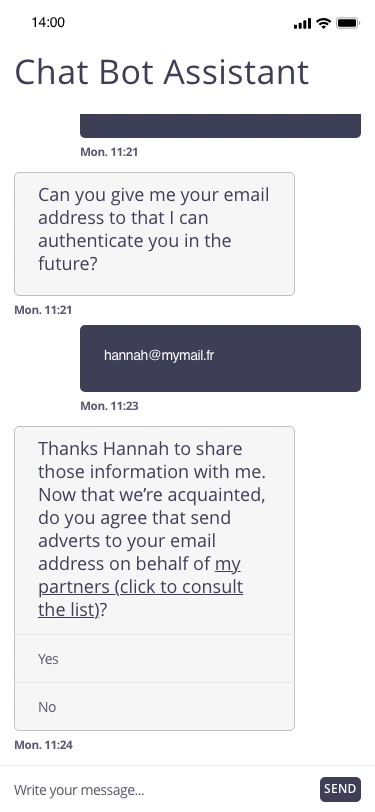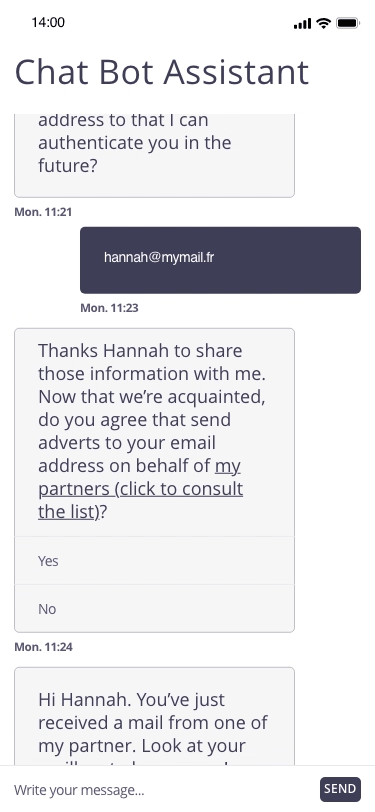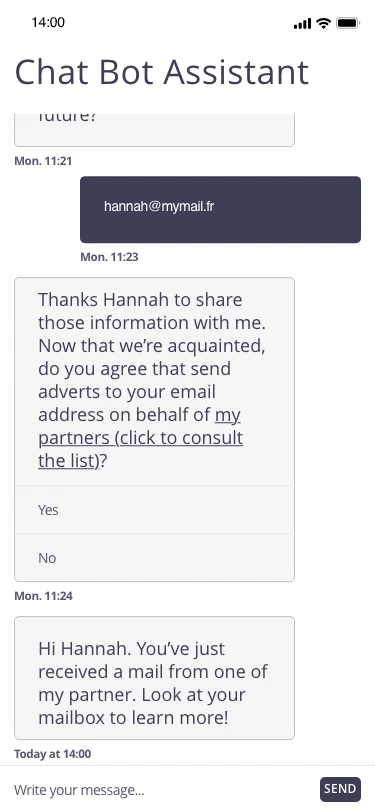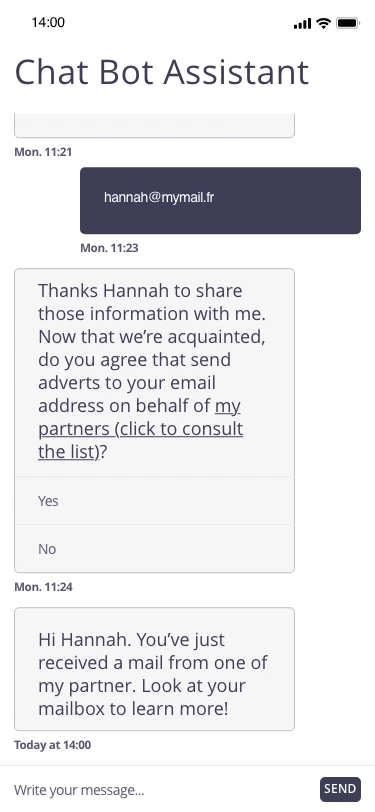
Possible approach (animated example)
Consent must be informed
Providing information to the data subjects before obtaining their consent is necessary to allow them to take decisions with full knowledge of the facts, to understand what they are consenting to and to know how to withdraw their consent. If the controller does not provide accessible information, the user’s control over her data may be insufficient.
The user must in particular know who is providing the service (data controller), the purposes of processing, the categories of collected data, the right to withdraw consent, etc.
To learn more about how to transfer information to the user, consult the page on how to inform data subjects.
Find out more
If you want to find out more about consent, you can consult the links below:
Legal Basis GDPR
Article 6 of the GDPR bearing on the “lawfulness of processing” presents the six legal bases possible on which data processing should be based to be lawful.
(fr) How to gather data subjects’ consent cnil.fr
A point-by-point explanation of the meaning of the notion of consent and information to be taken into consideration to ensure its validity.
(fr) Marketing by electronic means cnil.fr
An explanation of the conditions and principles of setting up consent in a marketing context (B-to-C and B-to-B).
Guidelines on consent pdf
Produced by the EDPB, this comprehensive document explains the concept of consent with a set of examples.
Explicit consent ico.org.uk
[consulted the 20 May 2019] An explanation of the concept of explicit consent by the ICO and illustrated by an example. This characteristic of consent is required in special cases, linked to the type of data processed or type of processing set up.
